The lung is the major part of the respiratory system.
It is a pyramid-like shape, an air-filled organ located on either side of the chest, supported by the thoracic cavity and surrounded by a pleural cavity.
Each lung divided into lobes, the right lung is bigger than the left, because of the heart placement in the chest.
The right lung has 3 lobes and the left lung has 2 lobes. Both lungs weigh around 1.3 kilograms, the right lung is heavier than the left lung.

Any organ in your body needs oxygen, the lung dose it easily through a process called gas exchange by taking in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide.
This process happened on alveoli, alveolus is a small sac of the lung where rapid gas exchange happened.
The respiratory system consists of the upper airway, and lower airway supplied by the pulmonary blood system.
The upper respiratory tract includes the mouth, the nose, the pharynx, the larynx, and the epiglottis.
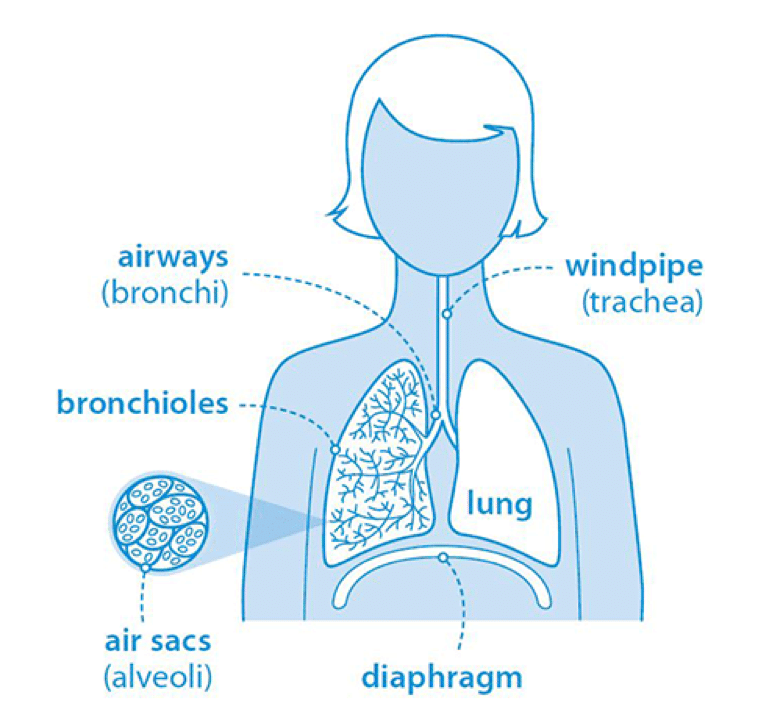
The lower respiratory tract includes the trach, the lung, and the diaphragm muscle.
We take air in and out of the lung by using negative pressure and muscle contraction to enhance gas exchange to achieve pulmonary ventilation.
Air enters the lungs passively by the contraction of the diaphragm and exhaled by the relaxation of the diaphragm combined by pressure ingredients.
During inhalation atmospheric air enters the lung consist of the high partial pressure of oxygen and low partial pressure of carbon dioxide.
The oxygen transported to the body while carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere.
Chest infection is an infection of the lungs or airways, there are two types of chest infection bronchitis and pneumonia.
Bronchitis is a lung disease that effected the bronchial tube lining, Bronchitis could be acute or chronic. The bronchitis is usually caused by a virus.
Pneumonia is an infection of the lung that causes alveoli to become inflamed and filled with fluid. Pneumonia is caused by bacteria.
Acute bronchitis happened most during autumn and winter, it is the most common type of chest infection.
Acute bronchitis affecting around 4.5% of people every year.
Pneumonia is most common during autumn and winter, it is a less common type of chest infection in adult but in older people above 65, it is four times higher.
Recurrent chest infection or bronchitis can lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
You have to seek medical attention if:
- You can’t sleep well during the night because of cough
- You have a fever combined with a cough.
- You have shortness of breath and wheezing associated with productive cough.
- You cough blood.
Chest infection causes
Bronchitis most often caused by a viral infection and if untreated it may bring bacterial infection
- Influenza virus: the same virus that causes cold and flu may be the initial reason for bronchitis
- Smoking: cigarette smoking leads to chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Dust and pollution exposure: air pollution exposure can irritate the lung in which may lead to serious lung disease over time.
Chest infection sign and symptoms
Bronchitis sign and symptoms include breathing problems for either acute or chronic bronchitis
- Fever and chills.
- Runny nose.
- Sore throat.
- Shortness of breath and chest pain.
- Productive cough.
- Chest tightness and discomfort.
- Fatigue.
- Headache.
- Body itching.
Chest infection risk factors
Factors that increase the risk for bronchitis
- Cigarette smoking.
- Previous history of allergy or asthma
- Low immune system.
- Positive family history of chest disease.
Chest infection diagnosis
At the early stage of the disease or the disease onset, it is hard to distinguish between common cold and bronchitis.
But most of the time these diagnostic tools your doctor may suggest.
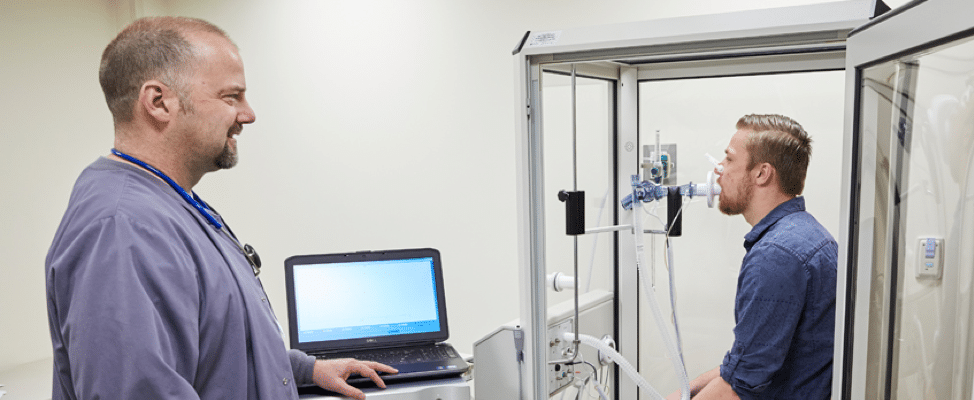

- Pulmonary function test: this type of diagnostic tool is used to evaluating lung mechanics and diagnosing pulmonary disease.
- Arterial blood gases: this type of diagnostic tool is used to evaluating your oxygen saturation and the level of carbon dioxide with a combination of Potential Hydrogen (PH). The normal value of oxygen saturation depends on the severity of the disease, carbon dioxide level ranges from 35-45mmHg, PH level range from 35 to 45 mmHg.
- Pulse oximeter: this type of diagnostic tool is used to measure oxygen saturation. If the reading was below 85% then your body tissues aren’t receiving enough oxygen. The pulse oximeter is a small device placed in the figure to transform your pulse to readings, these readings are oxygen saturation and heart rate. Oxygen saturation is the estimation of arterial oxygen saturation and the normal value of SPO2 is ranging from 100% to 95%. Below this range is hypoxia, low oxygen of the body tissue.
- Chest X-Ray: this type of diagnostic tool is used to evaluate the lung and determine wither you have fluid in the lung due to heart problems or another type of disease as an infection. Infection in the lung may cause pneumonia.
- Chest CT scan: this type of diagnostic tool is used to assess chest and to rule out if there is any hidden chest disease.
- Lung biopsy: this type of diagnostic tool is used if there is any suspicion of cancer or irregular chest tissues.
- Bronchoscopy: it is the direct inspection and examination of the upper and lower respiratory tract, this type of diagnostic tool is used to inspect the lung pathway and determine bleeding sites.
- Sputum culture and test: this type of diagnostic tool is used to determine the pathogenic organs that cause the chest infection and which type of antibiotic could cure the pathogen.
Chest infection treatment
The most chest infection can be treated without medical treatment such as cold and it ranged from mild to moderate.
A chest infection can be viral or bacterial and in severe cases, it is a medical emergency. Treatment can be medical or nonmedical:
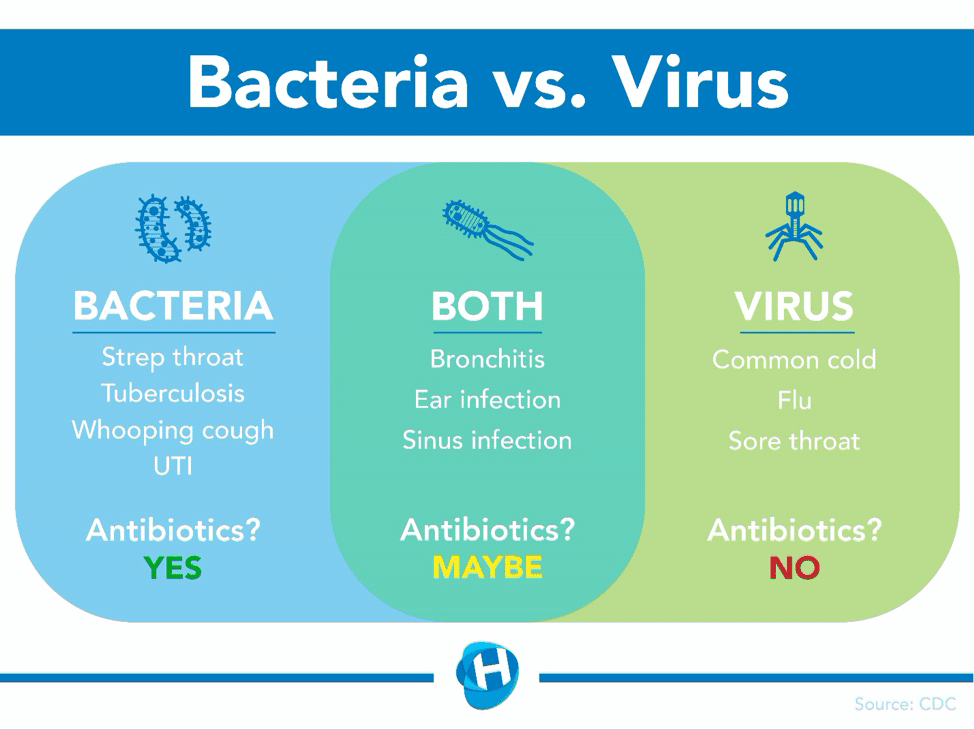
Medical treatment includes:
- Antibiotic medication: can clear out the infection, if the infection is bacterial.
- Antiviral medication: can clear out the infection, if the infection is viral
- Cough medication such as nebulizers and inhalers: cough suppressant to relieve cough and allergy
- Nebulizers and inhalers
Nonmedical treatment includes:

- Avoid tobacco smoking in order to avoid chest irritation.
- Use humidifier: warm and moist air will relieve cough and maculate the sputum.
- Stop activity and getting plenty of rest.
- Raise your head on a pillow while sleeping to keep your airway open
- Get a warm bath and inhale steaming to open the upper airway.
Jamil Qaryouti is a nursing specialist who graduated from J.U.S.T University in Jordan. Jamil has a wide verity of experience in cardiac diseases, pulmonary and neurological disease, former ICCU nurse in the Specialty Hospital in Jordan, former CNO of home care, founder of Jamil’s Home Health Corporation. Jamil is a medical educator. He believes spreading the information makes the world better.