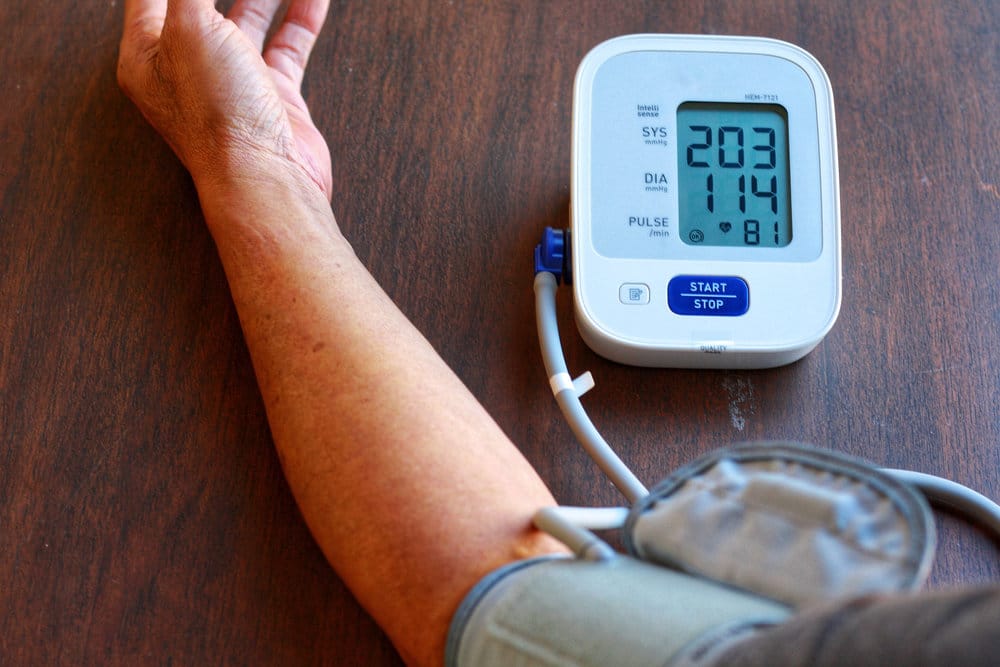
Blood pressure is the force of blood pumped from the heart against the wall of arteries.
Blood pressure consists of two numbers, the top number is systolic pressure (measured when the heartbeats) the bottom number is diastolic pressure (measured when the heart rests between each beat).
Blood pressure is written as systolic pressure / diastolic pressure.
Maximum pressure (systolic pressure) for most adults at rest is within the range of 100-130 millimeters mercury (mmHg), while minimum pressure (diastolic pressure) for the most adults during rest is within 60-80 mmHg.
High blood pressure is present if the reading was 130/80 mmHg or above for most adults at rest, for more than one reading.
High blood pressure also known as hypertension is a medical condition if untreated it may cause serious cardiac problems.
You will be at risk for coronary artery disease, stroke, heart failure, heart arrhythmias, brain damage, and kidney disease.
Especially hypertension does not make significant symptoms.
Thus, you have to check your blood pressure regularly to be on the safe side.
Hypertension classification
- Primary hypertension caused by nonspecific lifestyle and genetic factors.
- Secondary hypertension induced by endocrine disorder, kidney disease, and birth control pills.
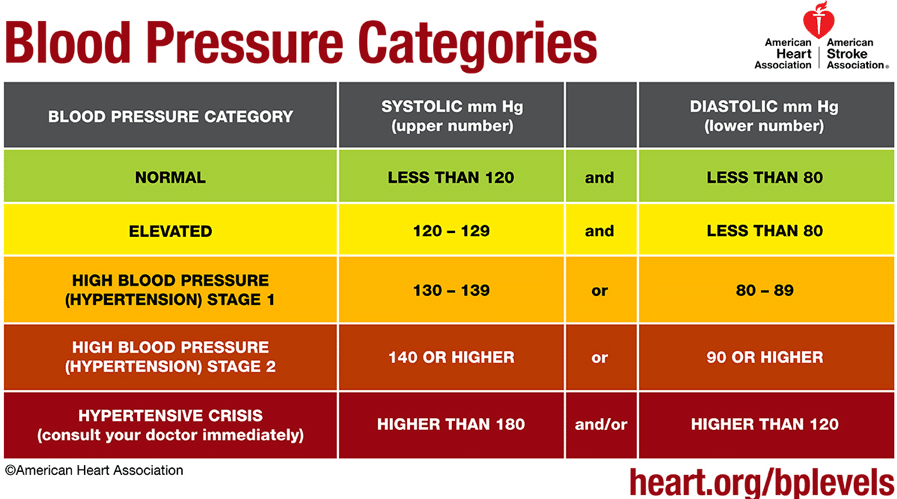
Blood pressure categories
- Normal pressure: below 120/80 mmHg.
- Elevated blood pressure: 129/80 mmHg, and it tends to be worse over time if left untreated.
- Stage one hypertension: above 130/80 mmHg and below 140/90 mmHg.
- Stage two hypertension: above 140/90 mmHg.
- Hypertension crisis: above 180/120 mmHg, medical emergency.
Over the years, researches and most studies have found that high systolic pressure showed a great risk of developing stroke and heart disease among people older than 65.
High Blood Pressure Causes
Several things may play the role of high blood pressure, but the exact cause still unknown, these things include:
- Stress
- Aging
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Lack of exercise
- Positive family history
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Eating too much salt
- Sleeping apnea
- Insulin resistance
- Caffeine consumption and vitamin D deficiency are less clear
High Blood Pressure Diagnosis
Hypertension is diagnosed based on a persistently elevated resting pressure above 130/80 mmHg.
The American heart association recommends at least three resting measurements on at least two separated health care visits.
To confirm the diagnosis of hypertension.
The Health care provider should include initial assessment such as family history, physical exam, electrocardiogram, and lab investigation regarding kidney function test, and on some cases chest X-Ray to determine the heart muscle
Blood pressure measurement technique tips:
- Sit quietly and relax for at least 5 minutes.
- Sit with your back supported.
- Sit with your feet on the floor.
- Sit with your legs uncrossed.
- Sit and elevate your cuffed arm toward the level of the hart.
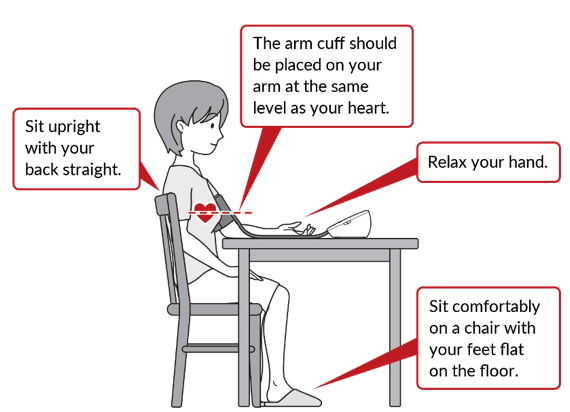
Inappropriate measurement of blood pressure can change the reading of 10 mmHg, which can lead to a misdiagnosis of hypertension.
The Symptoms..
Symptoms are vary based on the severity of the disease, there are certain symptoms including:
- Shortness of breath
- Headaches ( especially at the back of the head and morning )
- Fatigue
- Chest pain
- Nose bleeding
- Vision problems
- Fainting episodes
- Ear problem ( hissing in the ears )

You are at risk to develop heart attack, brain injury or kidney failure. If you have any of these symptoms please visit your doctor immediately.
Hypertension can occur during pregnancy in a medical condition called preeclampsia.
Preeclampsia is a serious condition it begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy and following delivery.
It is characterized by an increase in blood pressure and the presence of protein in the urine.
Preeclampsia can lead to fatal complications for both the baby and the mother.
Treatment..
Treatment involves lifestyle changes and drug therapy
Lifestyle changes including:
- Quitting smoking
- Losing weight
- Reducing salt intake
- Changing eating habit by reducing fat diet and increasing vegetables and fruits diet
- Getting regular exercises
- Avoiding caffeine beverage before exercise activity

Drug Therapy
The Anti-hypertensive drug is recommended for elderly people and those with risk factors such as high cholesterol and diabetes. Your doctor will start the medicine based on your condition.
Various classes of hypertension medication
- Thiazide diuretics: called water pills, this class of medication reduces the body volume by eliminating sodium and water. Thiazide diuretics are the first-line treatment of hypertension.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: this class of medication work in relaxing the blood vessels as well as decrease the volume, this class of medication prescribed for people with kidney disease.
- Angiotensin 2 receptor blockers (ARBS): this class of medication work in relaxing the blood vessel and treating left-sided heart failure. This class appears to produce a less adverse effect than ACE in people with kidney disease.
- Calcium channel blockers (CCB): this class of medication effective against large blood vessel stiffness. Also, it used for altering the heart rate (decrease heart rate).
There is another type of medication your doctor may describe if the above medications combination did not help to lower your blood pressure.
Further References
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/symptoms-causes/syc-20373410
https://www.healthline.com/health/high-blood-pressure-hypertension
Pulmonary Edema Causes and Treatment
Jamil Qaryouti is a nursing specialist who graduated from J.U.S.T University in Jordan. Jamil has a wide verity of experience in cardiac diseases, pulmonary and neurological disease, former ICCU nurse in the Specialty Hospital in Jordan, former CNO of home care, founder of Jamil’s Home Health Corporation. Jamil is a medical educator. He believes spreading the information makes the world better.