What is Pulmonary Edema? what causes it? and how can we treat it?
The lung is the major part of the respiratory system. It is a pyramid-like shape, an air-filled organ located on either side of the chest, supported by the thoracic cavity and surrounded by a pleural cavity.
Each lung divided into lobes, the right lung is bigger than the left, because of the heart placement in the chest.
The right lung has 3 lobes and the left lung has 2 lobes. Both lungs weigh around 1.3 kilograms, the right lung is heavier than the left lung.
Any organ in your body needs oxygen, the lung dose it easily through a process called gas exchange by taking in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide.
This process happened on alveoli, alveolus is a small sac of the lung where rapid gas exchange happened.
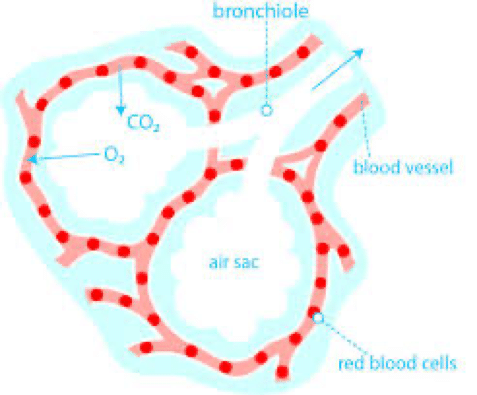
Simply, Pulmonary edema is the accumulation of fluid in the alveoli, alveoli play a great role of keeping us a life by taking oxygen from air via upper respiratory tract through inhalation.
Upper respiratory tract include nose, pharynx, and portion of larynx, and to get rid of carbon dioxide from the body via lower respiratory tract through exhalation.
While lower respiratory tract includes bronchioles, bronchial, trach and vocal cords.
Pulmonary Edema Causes
the heart is greatly rePulmonary edema. Because of this causes are based on heart-related and none-heart-related pulmonary edema.
Read more about heart diseases.
Heart-related causes:
- Coronary artery disease: a gradual buildup of plaque and total occlusion of the coronary artery due to clot formation, in which the heart failed to pump blood, and blood return into your lung gradually causing pulmonary edema.
- Valvular problems: valves regulate blood flow in the heart. The mitral valve regulates blood flow in the left side of the heart. Mitral valve disease represented by either stenosis (not open completely) or not close completely (regurgitation). In both cases, this pulmonary vein affected and cause fluid accumulation and pulmonary edema.
- High blood pressure (hypertension): high blood pressure if not treated will cause enlarge of the left ventricle, which leads to pulmonary edema.
Non-heart-related causes:
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): this respiratory problem happened very fast and rapid. It is a life-threatening problem. This critical problem happens when the lung inflamed because of fluid leakage into the lung.
- Adverse drug reaction: heroin or cocaine with aspirin can cause a very bad reaction. This reaction has a direct effect in the lung, this causes a fluid buildup of the lung and pulmonary edema.
- Chest infection: viral infection such as dengue virus and hantavirus, these two types of viruses can cause serious inflammation of the lung. Lung Inflammation caused a fluid leak and fluid accumulation into the lung.
- High altitudes: people who climbed the mountain are at risk of developing high-altitude pulmonary edema.
- Inhalation of toxic gases.
- Pulmonary embolism: a clot may travel from the leg to the lung. Clot formation on the pulmonary system leads to cardiac problems and pulmonary edema.
- Cardiomyopathy: enlarging the heart muscle due to left ventricle damage. The heart may not be able to respond to the situation that needs it to work harder when left ventricle impaired fluid backs up to the lung.
- Neurogenic causes: seizures and lung trauma can cause pulmonary edema.
- Negative pressure pulmonary edema: negative pressure rupture chest capillaries and increase pulmonary blood volume.
Pulmonary Edema Symptoms
A lot of symptoms might happen regarding pulmonary edema and left ventricle failure, symptoms can be new (acute) or old (chronic).
Acute symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath.
- Extreme shortness of breath with activity.
- Palpitation a rapid irregular heart rhythm.
- Restlessness.
- Difficult to laying down because of drowning feeling.
- A productive cough may be mixed with blood.
- Wheezing breathing.
- Cold skin.
- Blue lips
Chronic symptoms include:
- Fatigue.
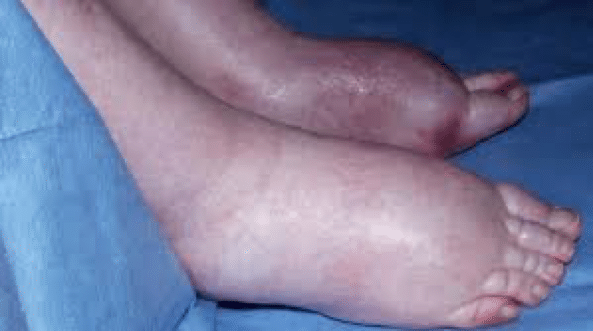
- Lower limb edema.
- Rapid weight gain.
- More shortness of breath.
- Difficult breathing when laying down.
- Wheezing breathing.
Diagnosis
A lot of diagnostic tools may consider, there is no single tool to confirm the disease. These tools include:
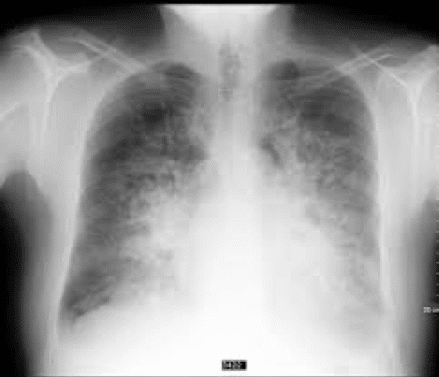
- Chest x-ray: this kind of diagnostic tool helps determine to wither you have fluid in the lung due to heart problems or another type of disease like an infection. Infection in the lung may cause pneumonia.
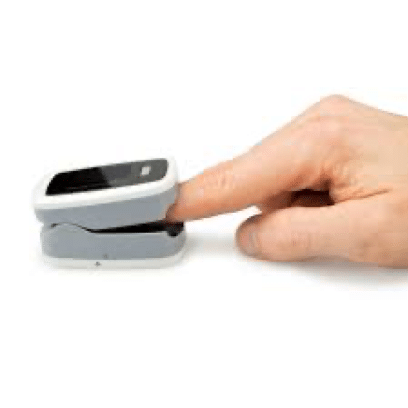
- Pulse oximeter: a small device placed in your figure to transform your pulse to readings, these readings are oxygen saturation and heart rate. Oxygen saturation is the estimation of arterial oxygen saturation and the normal value of SPO2 is ranging from 100% to 95%. Below this range is hypoxia, low oxygen of the body tissue.

- Blood test: arterial blood gas to check the value of saturated oxygen and carbon dioxide level. Carbon dioxide ranged from 35-45mmHg. In pulmonary edema, this reading could be high regarding the severity of the disease. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is the best test to diagnose heart-related pulmonary edema. Thyroid and kidney function to diagnose non-heart-related pulmonary edema. Also, kidney function and complete blood count.
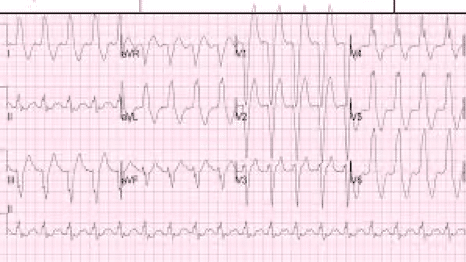
- Electrocardiogram: this type of diagnostic tool is so important because it reveals your heart conduction system, and could show any ischemic changes in the coronary artery. Ischemia is the decrease in blood supply inside blood vessels due to the total or partial blockage of blood vessels.
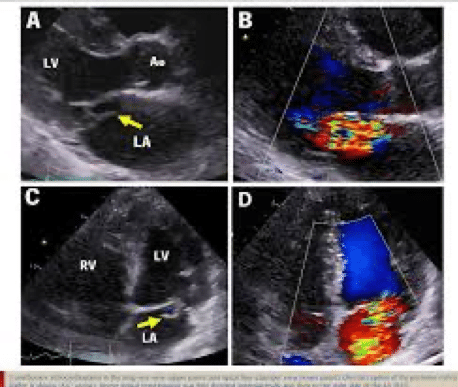
- Echocardiogram: this type of tool uses a transducer to generate sound waves that reflect images from your heart to check heart valves, ventricular wall, and fluid around the heart and blood flow through the heart chamber.
- Cardiac catheterization: if these diagnostic tools uncover the cause of pulmonary edema, it is an invasive procedure which a large catheter inserted from your major vein such as femoral, brachial, and radial to your heart to see the image of coronary arteries.
Treatment
- Oxygen therapy: the first treatment of pulmonary edema and shortness of breath is oxygen therapy. Oxygen delivered from tubes resting in the nose called nasal cannula or in the face called face mask or direct on the trachea called endotracheal tube. Based on the severity of the disease one of these O2 supplements applied.
- Diuretics: called water pills, this medication reduces the body volume by eliminating sodium and waterand reducing fluid accumulation on the lung.
- Morphine: this medication reduces anxiety and pain-related shortness of breath.
- Vasodilators: this medication dilated your coronary vessels and reduce the heart workload. Two types of vasodilator preload dilator and afterload dilator.
Further References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pulmonary_edema
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009
Jamil Qaryouti is a nursing specialist who graduated from J.U.S.T University in Jordan. Jamil has a wide verity of experience in cardiac diseases, pulmonary and neurological disease, former ICCU nurse in the Specialty Hospital in Jordan, former CNO of home care, founder of Jamil’s Home Health Corporation. Jamil is a medical educator. He believes spreading the information makes the world better.







1 Comment